

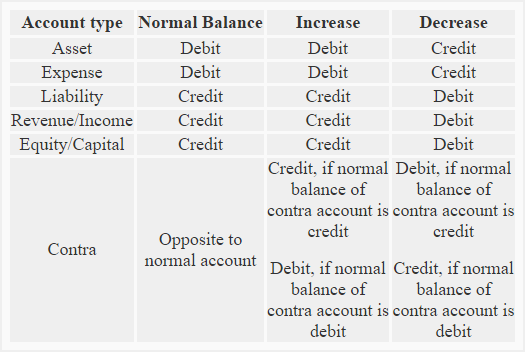
Therefore, those accounts are decreased by a debit.Īfter a while, you will have the rules for debits and credits for each type of account committed to memory, but for now, you can always determine which accounts are increased by a debit (and therefore decreased by a credit) and which accounts are increased by a credit (and therefore decreased by a debit) by using this bit of logic: \text An increase to an account on the right side of the equation (liabilities and equity) is shown by an entry on the right side of the account (credit). Therefore, those accounts are decreased by a credit. Sam 8,000 KES on credit.Some accounts are increased by a debit and some are increased by a credit. An increase to an account on the left side of the equation (assets) is shown by an entry on the left side of the account (debit). Sham started a business with Rs.60,000 cash. In the below example, we have listed different types of transactions along with the type of accounts and details of debit/credit after applying the accounting rules.
Sale of goods worth Rs.35,000 to Melon Ltd.The Purchase Account is a Nominal account and the Creditors Account is a Personal account. Applying Golden Rule for Nominal account and Personal account: Purchase goods worth Rs.50,000 from Apple Ltd.Now applying the golden rules to each of the transactions we will get the following journal entries :īoth Bank and Cash are real accounts and so the Golden rule is:

Nominal Account – Income AccountReal Account – Asset Account Nominal AccountReal Account – Asset accountĮarn Rs.3,000 as interest on Bank account Nominal Account -Income AccountPersonal Account – Debtors Account Nominal Account – Expense account personal Account – Creditors account Purchase goods worth Rs.50,000 from Apple Ltd. Real Account – Asset account real Account – Asset account It earns Rs.3,000 as interest on a bank account.įirst of all, let us identify the accounts involved in these transactions and classify them into the different types of accounts: Transaction.It pays Rs.12,000 as Rent for its premises.It sells goods worth Rs.35,000 to Melon Ltd.It buys goods worth Rs.50,000 from Apple Ltd.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
